Anoxic Biowash for Biogas Desulfurization as a Contribution to the Climate Future
Development of a method to convert ammonium from digestate into nitrate and its reuse as an oxygen donor for biological oxidative biogas desulfurization

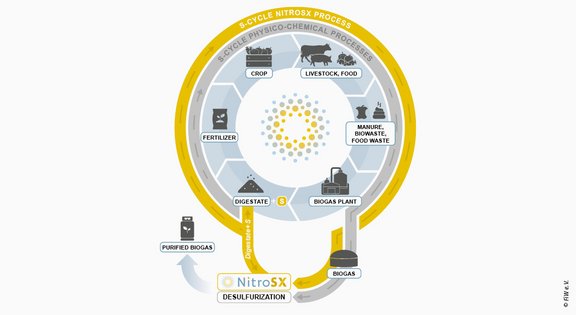
In the face of ambitious national and European efforts to reduce anthropogenically induced climate change by at least 55 % compared to 1990 emissions and achieve national climate neutrality by 2045, renewable (RE) and biogenic energy sources have gained significant importance. In this context, biogas, as a continuously producible fuel, plays a crucial role. The NitroSX process aims to enable the utilization of available streams in the biogas plant. In this way, the process is expected to contribute to the sustainability and economic viability of biogas plant operation.
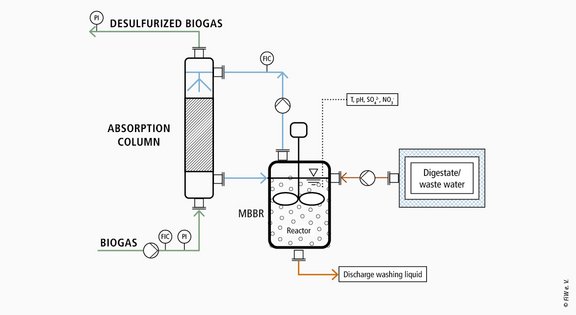
As part of the NitroSX projects, a pilot plant was designed and built on a container scale, which was subsequently tested in an agricultural biogas plant. The pilot plant is operated with digestate and biogas from a biogas plant to ensure realistic and practical operating conditions. In this process, naturally occurring microorganisms (chemolithotrophic bacteria) and nutrients in the digestate are used to convert reduced sulfur compounds for energy production. In the biological desulfurization process under anoxic conditions, these microbiological strains are used to reduce H2S in biogas using nitrate (NO3–). The conversion occurs step by step from reduced sulfur, through elemental sulfur to sulfate.